15/11/2018 - 19/03/2019
Life Sciences
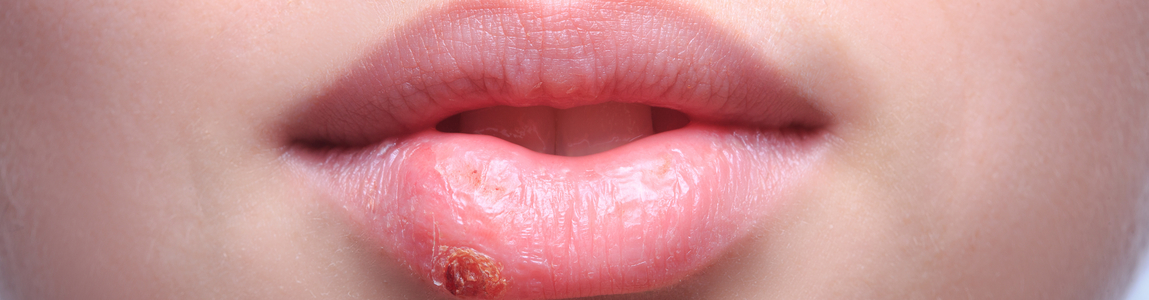
A Potential Risk Factor for Alzheimer’s Identified in the Herpes Simplex Virus
Monday, 18 March 2019 - 12:00pm
The research project, coordinated by the Department of Public Health and Infectious Diseases at Sapienza University in collaboration with the CNR, the Sacred Heart Catholic University and IRCCS San Raffaele Pisana, suggests that herpes simplex virus may be a risk factor for the onset of Alzheimer’s disease. The study, which opens new routes for prevention and therapy, has been published on PLoS Pathogens
Protecting Animal Culture, a New Strategy for Species Conservation
Tuesday, 12 March 2019 - 1:15pm
The social life of animals represents a real expression of culture: this is what was stated by a new international study in which Paolo Ciucci of the Charles Darwin Department of Biology and Biotechnology participated. The results of the research, published in the journal Science, can support the planning of concrete protection interventions and the development of adequate and effective conservation policies
Magnetic Fields for Muscular Atrophy: New Method Slows Down Muscle Decline and Improves Functionality
Monday, 11 March 2019 - 1:00pm
For the first time, four Departments of Sapienza have experienced the application of the magnetic field on the muscles of patients suffering from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), highlighting the positive effects of stimulation. The results, which open new perspectives to combat muscular atrophy, were published in the journal Scientific Reports
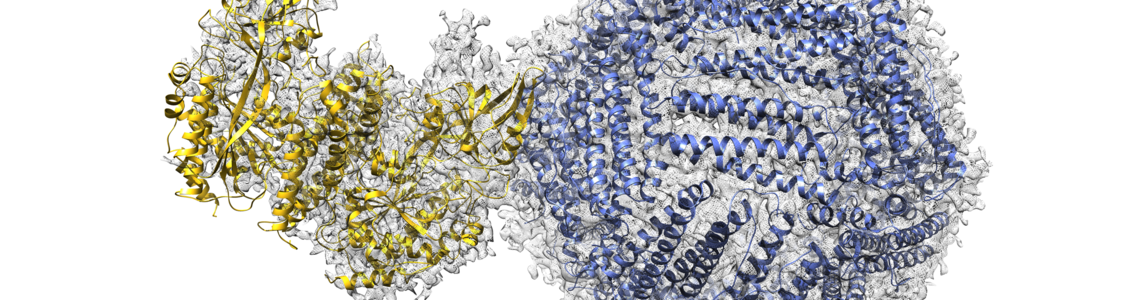
Sapienza Researchers Find the Key that Grants Iron Access to Cells
Friday, 8 March 2019 - 11:15am
Thanks to the revolutionary technique of cryogenic electron microscopy, a group of researchers from the Sapienza “A. Rossi Fanelli” Department of Biochemistry and the IIT@Sapienza Lab observed how the mechanism through which cells incorporate iron is the same used by viruses to infect them. The results, published on Nature Communications, pave the way to the development of precision drugs against viruses and tumours
Identified Proteins Working two Jobs
Thursday, 21 February 2019 - 12:00pm
Two proteins involved in mRNA splicing have a second job. During cell division, when splicing is interrupted, they directly mediate chromosome segregation to the daughter cells. The study, which could identify new anti-tumor targets, has been conducted by researchers at Sapienza University and at the Institute of Molecular Biology and Pathology of the CNR in Rome. The results have been published in the journal eLife
Neurodegenerative diseases: Discovered the Role of RNAs in Toxic Protein Aggregates
Wednesday, 13 February 2019 - 1:00pm
The result, published in the journal Cell Reports, reveals that specific RNAs are involved in Fragile X Tremor Ataxia Syndrome, a degenerative disease that affects the nervous system. The study conducted by Sapienza researchers and the Center for Genetic Regulation in Barcelona, can improve our understanding of complex diseases by providing hopes for new treatments
Fight Against Cancer: The Discovery of a New Target Involved in the Tumoral progression
Thursday, 31 January 2019 - 3:00pm
The research, conducted by the "Charles Darwin" Department of Biology and Biotechnology at Sapienza in collaboration with the Italian Institute of Technology, has identified a specific circular RNA with a crucial role in the development of rhabdomyosarcoma, a childhood tumor that affects skeletal muscle. The research, which opens up new perspectives for the treatment of cancer, has been published in the journal Oncogene
The Neanderthal from Altamura: On the Shoulders of the Past
Thursday, 20 December 2018 - 3:00pm
An international research team coordinated by Sapienza showed, through the reconstruction of the scapula with 3D imaging techniques, that a skeleton of the species Homo neanderthalensis, the most ancient and complete ever found, presents characteristics of the shoulder that distinguish it from the other Neanderthals as well as from our species Homo sapiens. The study is published in the journal Quaternary Science Reviews
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Induced Seismicity: How it Works and How to Reduce Hazard
Friday, 15 March 2019 - 12:00pm
A new research project developed by researchers at the Sapienza Department of Earth Sciences has improved our knowledge of the dynamic of earthquakes generated by the reintroduction of wastewater fluids into the subsurface during the extraction of hydrocarbons. The results, which are fundamental for the development of activities that will help in reducing the hazard of induced seismicity, have been published on Science Advances
Innovative Applications of Nanoporous Materials for the Environment: From Water Purification to Rechargeable Mechanical Batteries
Tuesday, 12 February 2019 - 2:45pm
A research Group, coordinated by Carlo Massimo Casciola of the Sapienza Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, has employed advanced molecular simulation techniques to design nano-structured materials with controllable wetting or drying behaviour. The study, published on ACS Nano, represents a significant step forward in the engineering of porous materials for energetic and environmental applications
Stepping Back 110 Million Years in Time to Study the Signs of Ageing on Materials Elasticity
Tuesday, 29 January 2019 - 3:00pm
An international research project coordinated by Sapienza University has revealed how the elastic properties of amorphous systems evolve over time. The results, which have been published on The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, were obtained by “rejuvenating” an amber fossil and bringing it back to the moment of its formation
Saturn Formed First, and Rings Came Long After
Friday, 18 January 2019 - 10:00am
Saturn’s rings formed only 100 million years ago, when dinosaurs roamed the Earth. The new findings of Sapienza’s researchers, now published on Science online edition, are the last gift of Cassini before its final plunge in atmosphere of Saturn.
Soft Matter: The Microscopic Properties of Polymeric Spheres from Futuristic Applications
Wednesday, 28 November 2018 - 1:00pm
A new theoretical model, supported by experimental evidence was developed by researchers from the Physics Department of Sapienza in collaboration with the Institute of Complex Systems of the Cnr and the University of Lund (Sweden). The study, which sheds new light on the microscopic properties of soft colloidal particles and their possible use, has been published in the journal Nature Communications
Social Sciences and Humanities
GiochiAMO: A Programme to Promote Children’s Health through Play
Tuesday, 26 February 2019 - 12:00pm
The “Promotion and Prevention” Research Group, led by Giuseppe La Torre of the Sapienza Department of Public Health and Infectious Diseases, has developed “GiochiAMO,” an innovative model to promote health in primary school through the the transmission of knowledge and engaged learning through ludic activities such as cards, board games and active games into the didactic programme
Am I Dreaming or Awake?: the Dreamlike Experience of Narcoleptics
Monday, 4 February 2019 - 3:00pm
A team of researchers from Sapienza and the University of Bologna has identified the neural substrate of dreams in people affected by narcolepsy. The results of the study, which confirms for the first time the existence of shared brain mechanisms of the dream in both Non-REM and REM stages, have been published in the journal Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology