We Can Now Bio-Print Neurons
Bio-printing, a cutting-edge biomedical technique, makes use of biological ink – cells and products derived from biocompatible non-living material – to assemble 3D models of various types of biological tissue.
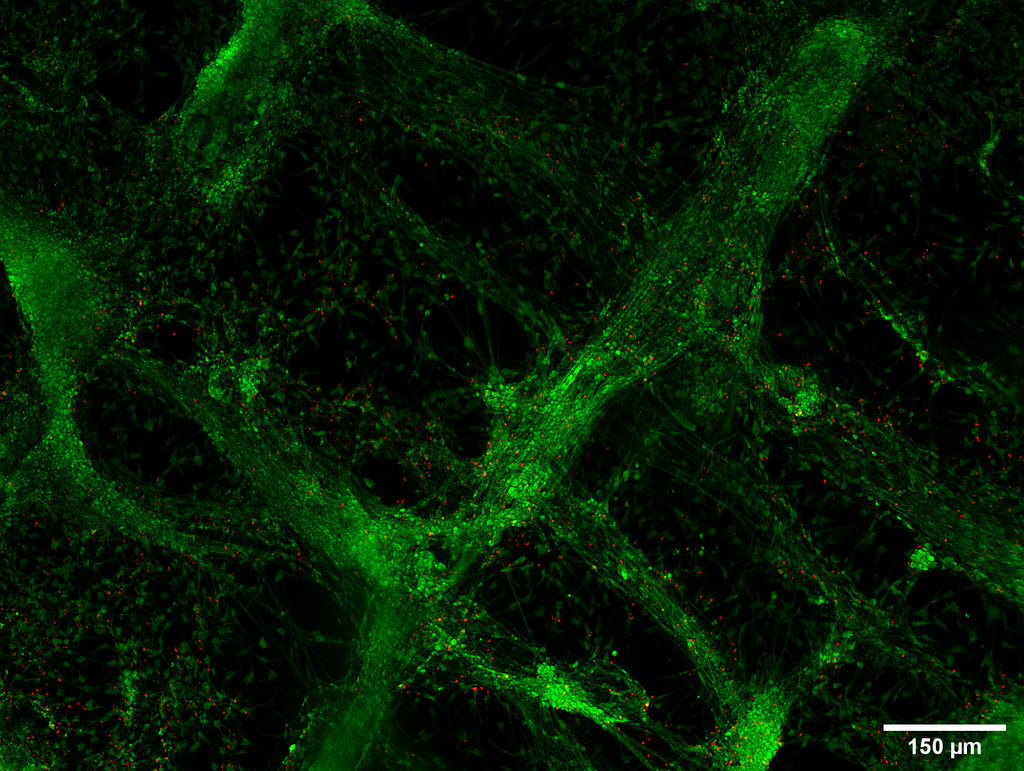
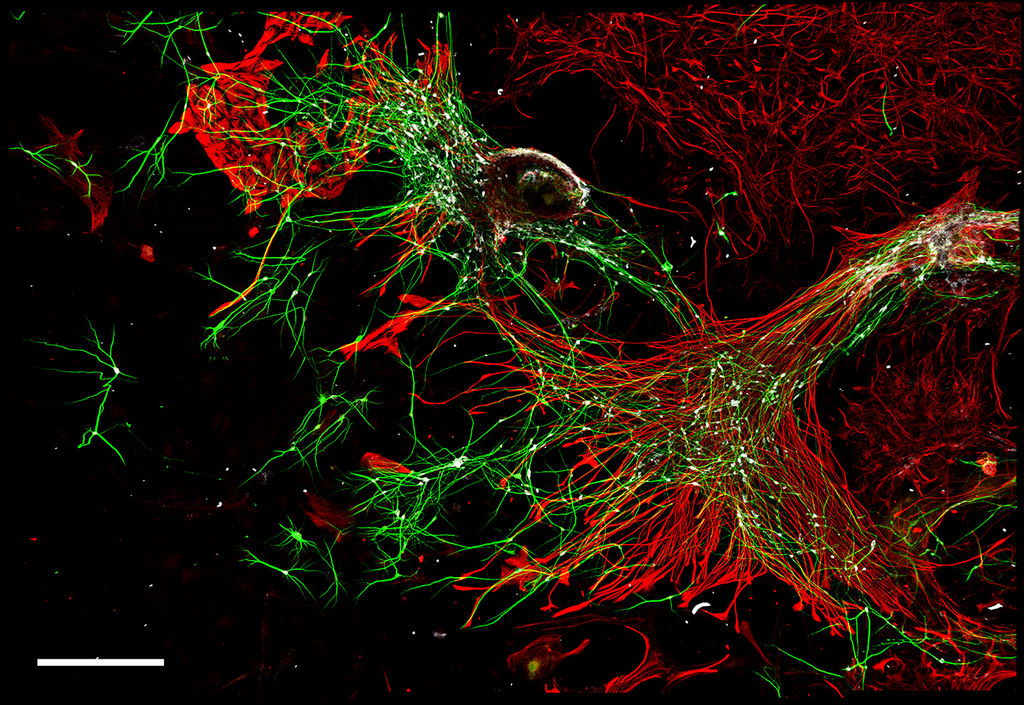
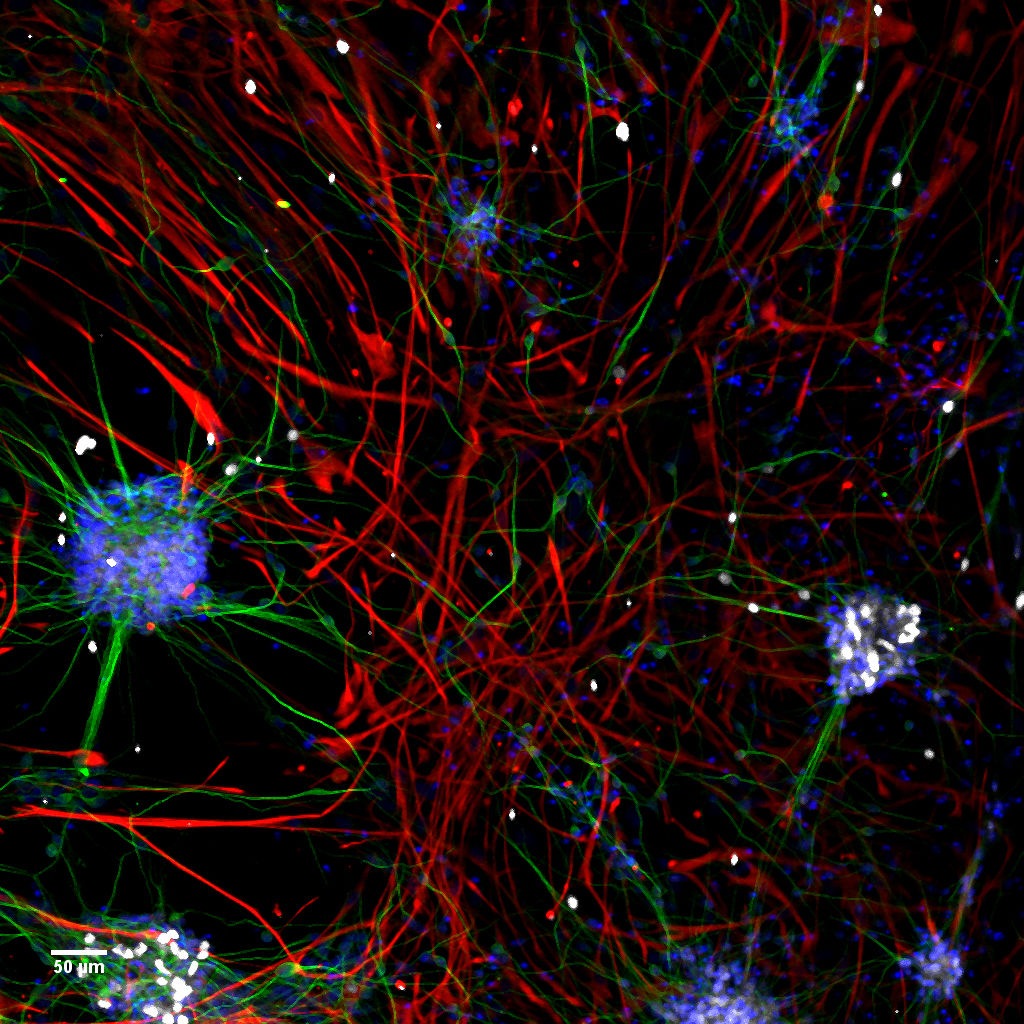
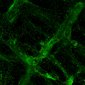
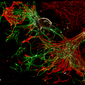
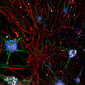
Model-cellular systems obtained through bio-printing processes are fundamental for the study of the nervous system in vitro, even due to their plastic properties. Recently, there have been various technological innovations in this field of research. In particular, there has been a shift from a classical approach in which cells are cultivated one layer at a time (2D) to three-dimensional (3D) models that provide more relevant information on the cytoarchitecture and interaction of brain cells.
The study, coordinated by Silvia Di Angelantonio and Alessandro Rosa, respectively from the Sapienza“Vittorio Espamer” Department of Physiology and Pharmacology and the “Charles Darwin” Department of Biology and Biotechnology, and researchers at the Rome IIT Centre (Centre for Life Nano Science, Italian Institute of Technology), in collaboration with a team from LaBioprinting IIT.
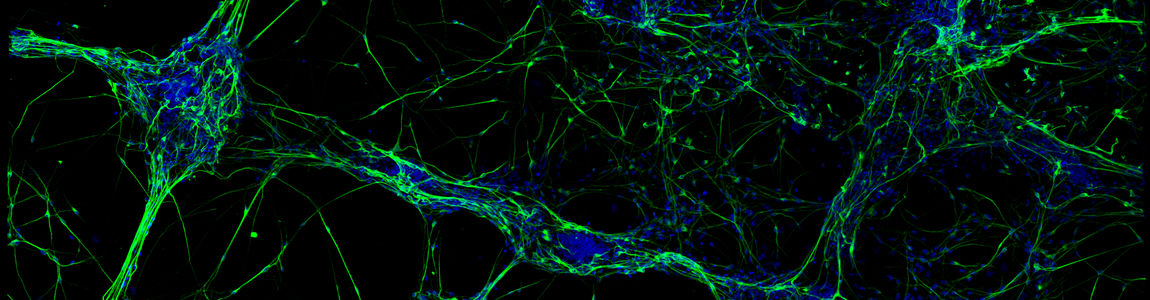
Thanks to their various abilities and converging interests, the researchers developed a new functional 3D neural construct by using a 3D microfluidic bioprinter and human cortical neurons derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPS cells). The results of the study were published on the Journal of Clinical Medicine.
“This new type of 3D neural construct with the molecular, morphologic and functional properties of neural networks,” explains Silvia Di Angelantonio, “can be used to model diseases and screen drugs.”
The innovative project will allow researcher to obtain important information on the mechanisms behind the physiological development and the pathologies of the central nervous system.
The research team has begun a process of technological transfer, promoted by IIT. The objective of HoMoLoG, as it will be called, intends to produce 3D-printed mini-organs to improve the study and treatment of a wide range of diseases. The start-up project has already received local and national recognition through its participation in the 2018 National Innovation Award and is presently receiving the interest of various investors and companies in the biomedical research sector.
References:
3D Bioprinted Human Cortical Neural Constructs Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells – Salaris, F. Colosi, C. Brighi, C. Soloperto, A. Turris, V. Benedetti, M.C. Ghirga, S. Rosito, M. Di Angelantonio, S. Rosa, A. Journal of Clinical Medicine (2 Ottobre 2019) DOI 10.3390/jcm8101595
Further Information
Silvia Di Angelantonio - silvia.diangelantonio@uniroma1.it
“Vittorio Espamer” Department of Physiology and Pharmacology
Alessandro Rosa - alessandro.rosa@uniroma1.it
“Charles Darwin” Department of Biology and Biotechnology